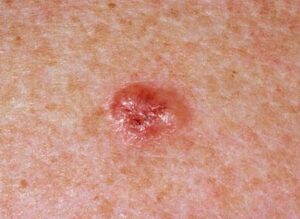
 One of the most common types of skin cancer is basal cell carcinoma (BCC). About 4 million people are diagnosed with BCC each year in the United States. Basal cells are one of the main types of cells in the top layer of the skin. BCC can occur when the basal cells get damaged by ultraviolet radiation, which leads to uncontrolled growth. Those who get sunburns are more likely to develop skin cancer.
One of the most common types of skin cancer is basal cell carcinoma (BCC). About 4 million people are diagnosed with BCC each year in the United States. Basal cells are one of the main types of cells in the top layer of the skin. BCC can occur when the basal cells get damaged by ultraviolet radiation, which leads to uncontrolled growth. Those who get sunburns are more likely to develop skin cancer.
Not all BCC skin cancers are the same. There are many subtypes that are diagnosed, and they behave and appear differently.
Basal Cell Carcinoma Subtypes
Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma
Making up over 60% of cases, nodular BCC appears as a white or skin-colored bump. They can be found on the face. Blood vessels become visible, and they may bleed. Nodular BCC can form a cystic pattern that may resemble a variant subtype called Cystic BCC.
Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma
Superficial BCC commonly shows up on the shoulders and the upper trunk. This subtype tends to grow slowly and is invasive. Superficial BCC presents as a patch or plaque and often has a threadlike border.
Morpheaform
Also called sclerosing, morpheaform BCC is an uncommon subtype that influences the production of fibroblasts within the dermis layer of the skin. The tumor is white or yellow and has a waxy texture. It is flat and often resembles a scar. Morpheaform BCC grows between collagen fibers and is difficult to diagnose.
Micronodular
Micronodular BCC tumors can be either flat or elevated. When flat, they have a yellow-whitish color. The tumors also have clear outlines and form a cluster of small rounded nodules. They are located on the skin of the back.
Infiltrative Basal Cell Carcinoma
This subtype forms as a thin cluster of basaloid cells that have a whitish color. Infiltrative BCC forms in the dermis layer located on the upper trunk or the face.
Pigment Basal Cell Carcinoma
Pigmentation can be observed in nodular, micronodular, and superficial BCC. It is abundant in melanin and melanophages and clinically appears either brown or black.
Basosquamous
Basosquamous, or metatypical BCC, is an infiltration growth pattern. It. can display features of both BCC and Sqaumous Cell Carcinoma skin cancer. This subtype is likely to be more aggressive than other subtypes.
Nodulocystic
The tumors in nodulocystic BCC are filled with fluid and have a blue-gray color. These cysts are often found within the tumor nests.
Microcystic
This subtype consists of keratin-filled cysts, and the nests of basaloid cells are located in the reticular dermis. This subtype is rare and often found on the head or neck.
Clear Cell
Clear Cell BCC is an uncommon subtype that is defined by its clear cells. The cells show a deteriorating change occurring in the tumor.
Granular Cell
Similar to clear cell BCC, granular cell BCC shows a tumor’s regressive change. Cells containing small, pink granules are a sign that granular cell BCC is present.
Singlet Ring Cell
Singlet Ring Cell BCC is characterized by the cell’s singlet ring appearance.
Solitary Basal Cell Carcinoma
Solitary BCC develops in younger patients. While other variants of BCC are commonly induced by ultraviolet exposure, this subtype develops from embryonic fusion clefts in the skin.
Adenoid
The tumor cells are slow-growing and are often found on the scalp. They have a gland-like structure and have cystic spaces consisting of mucinous material.
Follicular
Tumor cells of this variant look similar to hair follicles. Also found in follicular BCC are small infundibular cysts and matrical cells. This subtype does not have any distinctiveness to be differentiated from other variants.
Infundibulocystic
This subtype is less aggressive and contains follicular and infundibula germs in the tumor. Tumors cells are usually small and have a low penchant to infiltrate over a long period of time.
Neurotropic Basal Cell Carcinoma
Tumors of this subtype can affect a person’s nervous system. Neurotropic BCC can result in pain and discomfort. It is difficult to remove through surgery due to its microscopic size.
Pleomorphic Basal Cell Carcinoma
Pleomorphic BCC develops on the head or neck. Pleomorphic cells are large and have mucin production. This subtype can have mononucleated or multinucleated tumors.
Rodent Ulcer
Patients develop rodent ulcer if thier BCC is left untreated. An ulcer grows in the center of the tumor, leaving a hole in the skin.
Effective treatments are available for patients diagnosed with BCC with high cure rates. If you would like to learn more about basal cell carcinoma, contact us today.
